Barking, biting, chewing and many other common canine behavior problems are often misunderstood or mismanaged by dog owners. Perhaps you are a new dog owner, considering buying a dog, or simply want to manage your dog better? A thorough understanding of the most common canine behavior problems is the first step in solving and preventing them. A solid foundation of dog obedience training will help you prevent or better control these problems. Here are 10 behavioral problems that dogs often have.
1. Barking
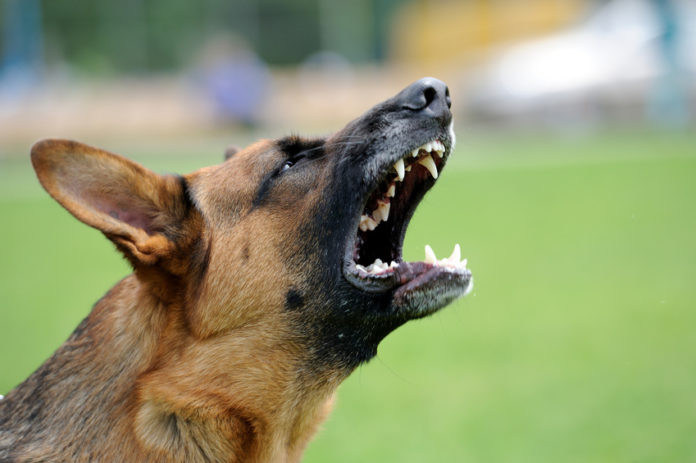

Most dogs bark, howl and moan to some extent. However, it is important to know that excessive barking is considered a behavioral problem. Before you try to find a solution to this problem, determine why your dog vocalizes first. The most common types of barking are as follows:
- Notify or alert its owner;
- Play and have fun;
- Seek attention;
- Express anxiety;
- Expressing boredom;
- Answer the other dogs.
Learn to control your dog’s excessive barking by being constant and patient. Also, consider teaching the commands of yapping and silence. Dedication and attention to detail can pay off.
2. Digging

If given the chance, most dogs will dig a little bit; it’s a matter of instinct. Some breeds, such as the terrier, are more inclined to dig holes because of their hunting instincts. In general, most dogs dig for these reasons:
- Boredom or excess energy;
- Anxiety or fear;
- The hunting instinct;
- The search for comfort (such as nesting or cooling);
- Hiding possessions (such as bones or toys);
- To escape from a place.
If your dog digs in your yard, it can be quite frustrating for you. Try to determine the cause of the excavation and then eliminate it. Spend more time with your dog and get him more exercise. If digging is inevitable, set aside a place where your dog can learn that it is acceptable to make holes, such as in a sandbox.
3. Anxiety
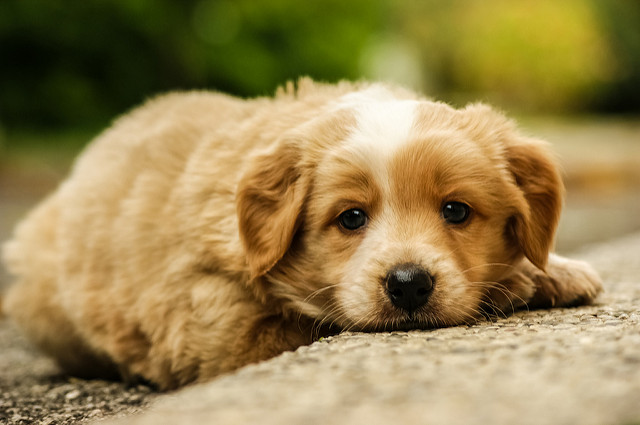

Separation anxiety is one of the most common canine behavioral problems. Manifestations include vocalization, chewing, urination and inappropriate defecation. Signs of separation anxiety include:
- The dog becomes anxious when the owner is preparing to leave.
- The misconduct occurs within the first 15 to 45 minutes after the owner leaves.
- The dog wants to follow the master at all times.
- The dog tries to touch the owner whenever possible.
True separation anxiety requires specialized training, behavior modification, and desensitization exercises. Medications may be recommended in extreme cases, but should only be used as a last resort.
4. Inappropriate urination

Inappropriate urination and defecation are among the most frustrating dog behaviors. They can damage parts of your home and make your dog unwanted in public places or in other people’s homes. It is very important that you first discuss this behavior with your veterinarian to eliminate health problems. If no medical cause is found, try to determine the reason for the behavior, which can be summarized as one of the following:
- Submitted/exciting urination
- Territorial marking
- Anxiety
- Seeking attention
Inappropriate elimination is inevitable in puppies, especially before 12 weeks of age. For older dogs, it’s another story. Many dogs need a serious change in their behavior to get rid of this habit, as you often have to change their perception of themselves.
5. Begging

Begging is a bad habit, but many dog owners encourage it. This can lead to digestive problems and obesity. Dogs beg because they love food. However, leftovers are not good for your pet. Yes, it is difficult to resist your pet’s gaze, but giving in “just this once” creates a long-term problem. When you teach your dog that begging is allowed, you are sending him the wrong message.
Before you sit down to eat, tell your dog to go to his place, preferably where he can’t stare at you. If necessary, confine your dog to another room. If he behaves well, give him a special treat only after you and your family have completely finished eating.
6. Hunting

A dog’s desire to chase moving objects is simply a demonstration of predatory instinct. Many dogs hunt other animals, people, and cars. All of this can have dangerous and devastating consequences. Although you can’t stop your dog from trying to pursue anything in motion, you can take steps to prevent any disastrous situation:
Keep your dog on a leash at all times (unless he is supervised directly indoors).
Train your dog to come when he is called.
Have a whistle or silencer on hand to attract your dog’s attention.
Stay tuned for potential triggers, such as joggers.
Your best chance of success is to prevent the pursuit from becoming uncontrollable.
7. Jump into the air
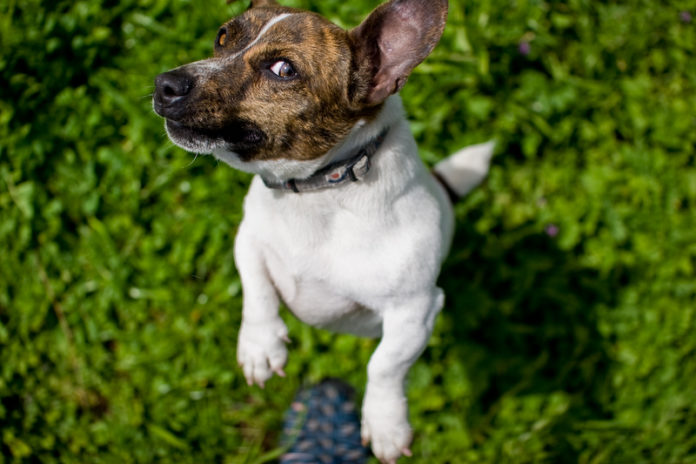

The puppies jump up to reach and greet their mothers. Later, they can get up to greet people. Dogs can also jump to exercise domination. A jumping dog can obviously be boring and even dangerous.
There are many methods to prevent a dog from jumping, but not all of them will be effective. Lifting a knee, grabbing the legs or pushing the dog back can work for some, but for most dogs, it sends the wrong message. Jumping up is often an attention-seeking behavior, so any recognition of your dog’s actions provides a reward.
The best method is to turn away and ignore your dog. Do not make eye contact, do not talk or touch your dog. When your dog is relaxed, reward him calmly. It won’t be long before your dog understands the message.
8. Bite
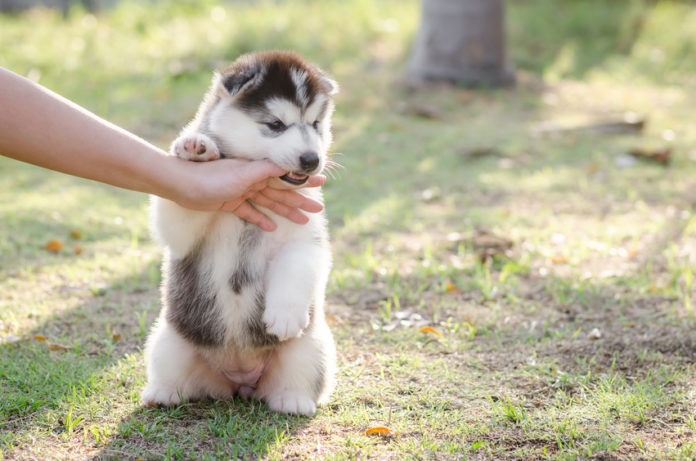

Dogs bite for reasons that can be traced back to the instinct and mentality of a pack. Puppies bite other dogs and people to explore their environment and take their place in the pack. Owners must show their puppies that jaw and bites are not acceptable by teaching them how to inhibit bites. Beyond the puppy’s behavior, the motivation to bite usually comes from the following:
- Fear or defensive
- Protection of property
- Pain or illness
- Affirmation of the dominant position
- The predatory instinct
Although some breeds are considered dangerous, many believe that race-specific legislation is not the solution. Owners and breeders are those who can help reduce the tendency of any type of dog to bite through appropriate training, socialization and breeding practices.
9. Aggressiveness
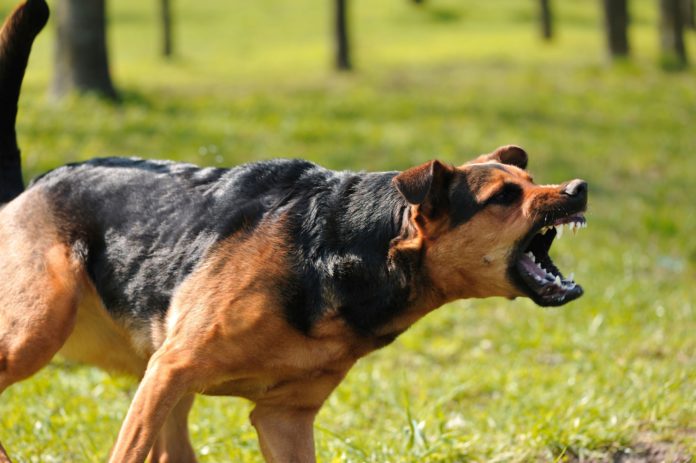

Dog aggressiveness manifests itself in growling and biting. It is important to know that every dog has the potential to become aggressive, regardless of his breed or history. However, dogs with a history of violence or abuse and those bred from dogs with aggressive tendencies are much more likely to behave aggressively towards people or other dogs. The reasons for aggression are basically the same as the reasons why a dog bites, but canine aggression, in general, is a much more serious problem.
If your dog has aggressive tendencies, consult your veterinarian first, as this may be due to a health problem. Then, seek the help of an experienced trainer or behaviorist. Serious measures must be taken to protect people and animals from aggressive dogs.
If you suspect that your pet is sick, call your veterinarian immediately. For health-related questions, always consult your veterinarian, as he or she has examined your animal, knows its health history and can make the best recommendations for your animal.
10. Chewing objects

Chewing objects is a natural action for all dogs. However, chewing can quickly become a behavioral problem if your dog causes destruction. The most common reasons dogs chew are as follows:
- The puppy’s teeth;
- Boredom or excess energy;
- Anxiety;
- Curiosity (especially puppies).
Encourage your dog to chew the right things by providing him with lots of chew toys. Keep your personal belongings away from your dog. When you are not at home, keep your dog in a cage or confined in a place where it is not likely to destroy your personal belongings.
If you catch your dog chewing the wrong thing, quickly correct your dog with a loud noise. Then replace the item with a chew toy. One of the most important things you can do is to make sure your dog gets plenty of exercises so he loses his energy and is stimulated in this way rather than turning to chew.


![[Photos] Why WD-40 Is Magic In Your Garden?](https://lifetonik.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/7/2019/08/WD40-Prices-Highres_Page_8_Image_0008-218x150.jpg)




![[Photos] Take A Look Of The Obama’s New Home Before It’s Banned](https://lifetonik.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/7/2019/07/Obama1-218x150.jpg)

![[Slideshow] Celebrity Homes: 21 Of The Most Luxurious](https://lifetonik.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/7/2019/07/Taylor-Swift-218x150.jpg)
![[Slideshow] More Parents Are Now Gluing Pennies to the Bottom of their Kid’s Shoes](https://lifetonik.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/7/2019/07/Keep-Them-Entertained-218x150.jpeg)
![[Photos] 20 Fashion Mistakes That Too Many Women Make!](https://lifetonik.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/7/2019/07/5-style-mistakes-that-make-you-look-frumpy-featured-218x150.jpg)


















![[Gallery] 25 Discounts For Seniors To Which You Are Entitled Without Knowing It](https://lifetonik.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/7/2019/08/EAZxECUXUAAvNZR-218x150.jpg)
![[Slideshow] Here’s the salary of every governor in the United States](https://lifetonik.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/7/2019/08/Charlie-Baker-218x150.jpg)
![[Photos] No One Will Want To Buy This House After Seeing These Pictures](https://lifetonik.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/7/2019/08/terrible-real-estate-photos-2-5c35e727c9f95__700-218x150.jpg)



